Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center
Bedform Sedimentology Site: “Bedforms and Cross-Bedding in Animation”

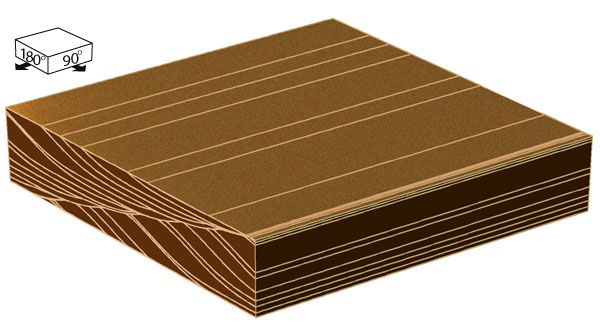
FIG. 21. Structure formed by bedforms that reverse direction of migration and undergo net migration.
RECOGNITION: This structure is similar to those produced by bedforms that reverse asymmetry while migrating (FIG. 22). The two kinds of structures can be distinguished, because reversals in asymmetry cause cross-beds to offlap and onlap the erosion surfaces within each set of cross-beds, whereas reversals in migration direction produce erosion surfaces with relatively concordant overlying beds, as shown here. Although the cross- beds are truncated at different elevations, the preserved parts of the cross-beds all have the same shape, because bedform shape does not change through time.
ORIGIN: This structure requires flow conditions similar to those of the preceding computer-generated example (reversing migration direction without net migration), except that, in the example illustrated here, the flow has a long-term transport asymmetry in order to cause net migration of the bedforms.