Home - Images - Products - Data - Publications - Contact
| |
 |
|
Northeast Region - Central Region |
|
The mid to outer continental shelf off Mississippi, Alabama, and northwest Florida were the focus of US Geological Survey (USGS), Pacific Seafloor Mapping Project (PSFMP) mapping efforts from 2000 to 2002 (Figure 1). In 2000 the PSFMP in cooperation with Univ. of New Hampshire, Univ. of New Brunswick, and the USGS Biological Resources Division (BRD) mapped the mid to outer shelf off Mississippi and Alabama (Figure 1) in an area known as the Pinnacles Region using a high-resolution multibeam echosounder (MBES). This survey took place to investigate the extent of "deep-water reefs" first suggested by Ludwig and Walton (1957). The reefs were initially described in water depths of 60 to 120 m (Ludwig and Walton, 1957) but the 2000 mapping found reef and hardgrounds to be much more extensive than previously thought (Gardner et al., 2001). It is critical to determine the accurate location, geomorphology, and types of the ridges and reefs that occur in this region to understand the Quaternary history of the area and to assess their importance as benthic habitats for fisheries.
In 2001, the PSFMP in cooperation with Univ of New Hampshire, Univ. of New Brunswick, BRD, and NOAA mapped the mid to outer shelf off Northwest Florida (Figure 1) to investigate whether the reef-like features mapped during the 2000 survey continue along the northwest Florida mid and outer shelf.
The "Head of De Soto Canyon" is the large outer continental shelf region previously unmapped between the 2000 and 2001 mapped areas. It was unknown whether the reefs of the Pinnacles region continue eastward into the head of De Soto Canyon region and connect with the ridges and reefs mapped on the northwest Florida outer shelf. The existence of carbonate-cemented Quaternary to Holocene sandstones along the western wall of the head of De Soto Canyon (Shipp and Hopkins, 1978; Benson et al., 1997) is of interest because of the potential benthic habitats they may represent. In the summer to 2002 the PSFMP in coorperation with Univ of New Hampshire, Univ. of New Brunswick, BRD, and Mineral Management Service (MMS) conducted a MBES survey of the Head of De Soto Canyon Region connecting the 2000 and 2001 mapped regions. Click on the above regional buttons to view that region's shaded relief bathymetry and acoustic backscatter imagery.
The multibeam bathymetry and acoustic backscatter data along with metadata and a GIS are published in U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report OF03-007.
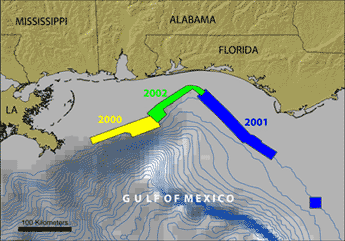
Figure 1. Northeastern Gulf of Mexico location map showing the areas mapped in 2000 (yellow), 2001 (blue), and 2002 (green) using high-resolution multibeam echosounders (MBES).
Benson, D.J., Schroeder, W.W., and Shultz, A.W., 1997, Sandstone hardbottoms along the western rim of De Soto Canyon, northeast Gulf of Mexico, Gulf coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans., v. 47, p. 43-48.
Gardner, J.V., Dartnell, P., Sulak, K.J., , and Calder, B., and Hellequin, L., 2001, Physiography and Late Quaternary-Holocene Processes of Northeastern Gulf of Mexico Outer Continental Shelf off Mississippi and Alabama, Gulf of Mexico Science v. 20, p. 132-157.
Ludwig, J.C and Walton, W.R., 1957, Shelf-edge calcareous brominences in northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Amer. Assoc. Petroleum Geologists, v. 41, p. 2054-2101.
Shipp, R.L. and Hopkins, T.S., 1978, Physical and biological observations of the northern rim of the De Soto Canyon make from a research submersible. Northeast Gulf Science, v. 2, p. 113-121.